sentinel学习笔记-1
Sentinel
Sentinel入门
Sentinel 是面向分布式服务架构的轻量级流量控制框架,主要以流量为切入点,从流量控制、熔断降级、系统负载保护等多个维度来帮助您保护服务的稳定性。
主要特性
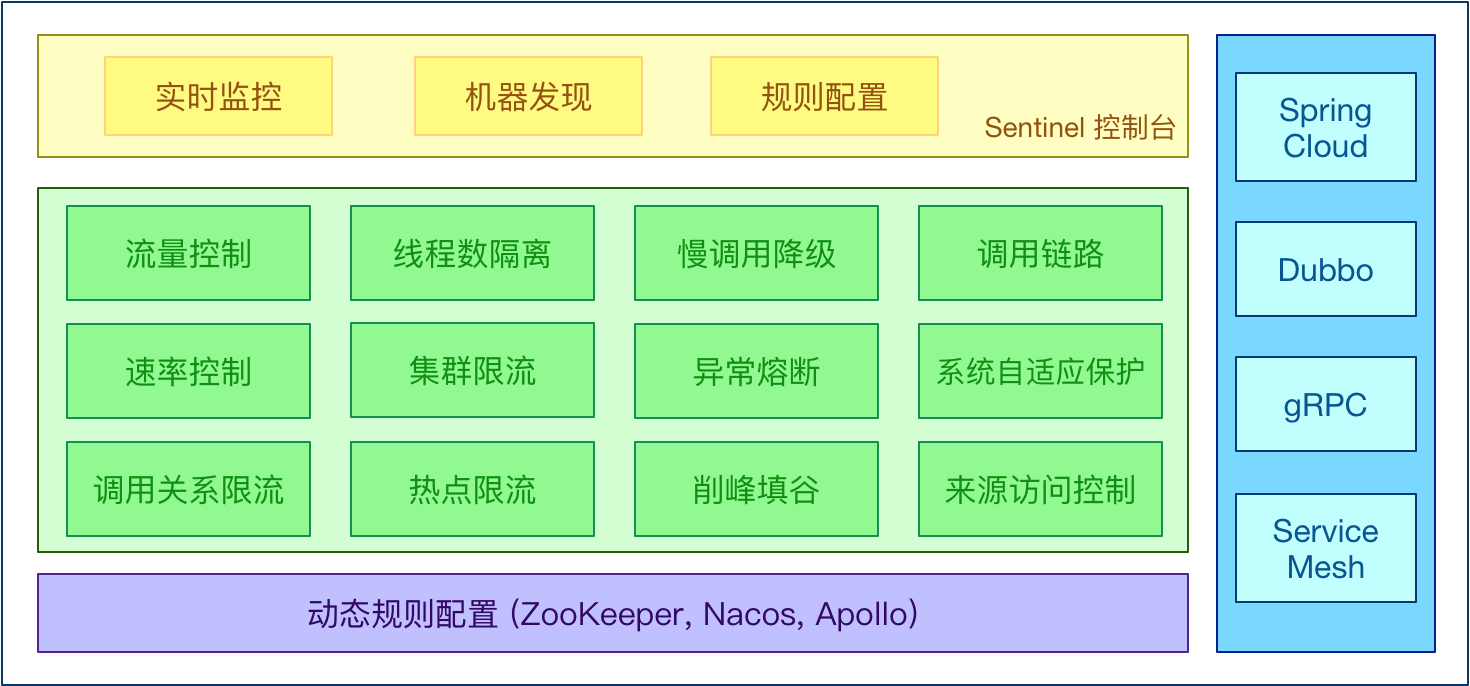
开始使用
引入sentinel依赖
1
2
3
4
5<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-core</artifactId>
<version>1.4.1</version>
</dependency>定义资源
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20public static void main(String[] args) {
// 配置规则.
initFlowRules();
while (true) {
Entry entry = null;
try {
entry = SphU.entry("HelloWorld");
// 资源中的逻辑.
// TODO something
System.out.println("hello world");
} catch (BlockException e1) {
System.out.println("blocked!");
} finally {
if (entry != null) {
entry.exit();
}
}
}
}定义规则
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13/**
* 每秒最多只能通过 20 个请求。
*/
private static void initFlowRules(){
List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<>();
FlowRule rule = new FlowRule();
rule.setResource("HelloWorld");
rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);
// Set limit QPS to 20.
rule.setCount(20);
rules.add(rule);
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}注解支持
在开发时一般不会去写sentinel的控制资源的逻辑,都是由AOP拦截来实现,所以sentinel提供了注解方式@SentinelResource的支持
需要添加注解依赖1
2
3
4
5<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-annotation-aspectj</artifactId>
<version>x.y.z</version>
</dependency>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26public class TestService {
// 对应的 `handleException` 函数需要位于 `ExceptionUtil` 类中,并且必须为 static 函数.
public void test() {
System.out.println("Test");
}
// 原函数
public String hello(long s) {
return String.format("Hello at %d", s);
}
// Fallback 函数,函数签名与原函数一致或加一个 Throwable 类型的参数.
public String helloFallback(long s) {
return String.format("Halooooo %d", s);
}
// Block 异常处理函数,参数最后多一个 BlockException,其余与原函数一致.
public String exceptionHandler(long s, BlockException ex) {
// Do some log here.
ex.printStackTrace();
return "Oops, error occurred at " + s;
}
}
1 | public SentinelResource { |